US Foreign Policy
The Foreign Policy Bureaucracy
Michael E. Flynn
Kansas State University
Updated: 2021-09-13
Lecture Overview
Historical Trends
What are bureaucracies?
Why do they matter?
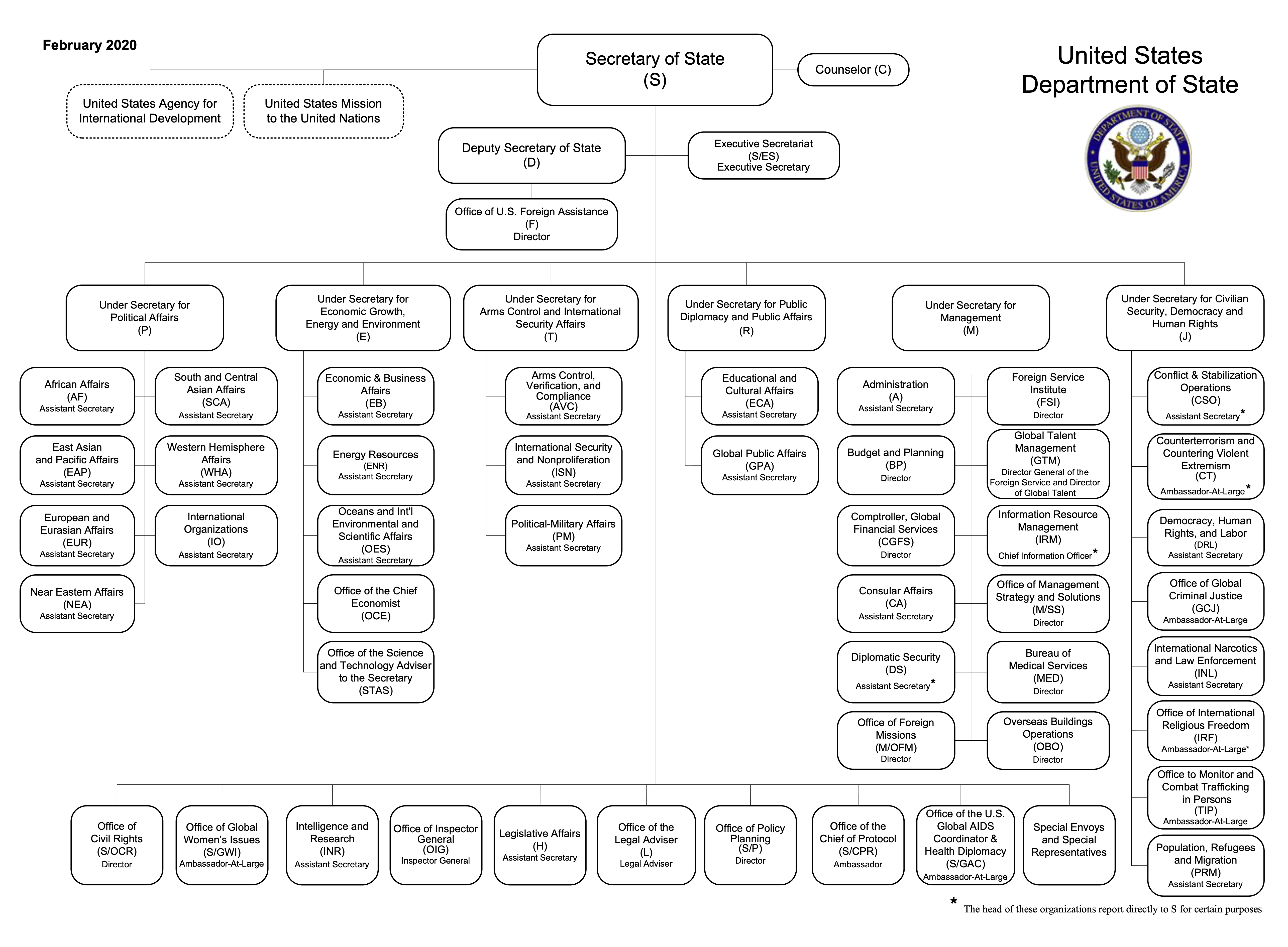
The State Department
Key Questions
How did the foreign policy buraucracy change between the pre- and post-War periods?
Why/How might suboptimal policy outcomes result from otherwise good actors following organizational mandates?
How are actors at different positiosn in a bureaucratic hierarchy able to exercise power and influence?
How has the State Department's role in foreign policymaking changed over time?
What Are Bureaucracies?
What Are Bureaucracies?
Executive bureaucracy before World War II
Very small
Creation of the Executive Office of the President (EOP) in 1939
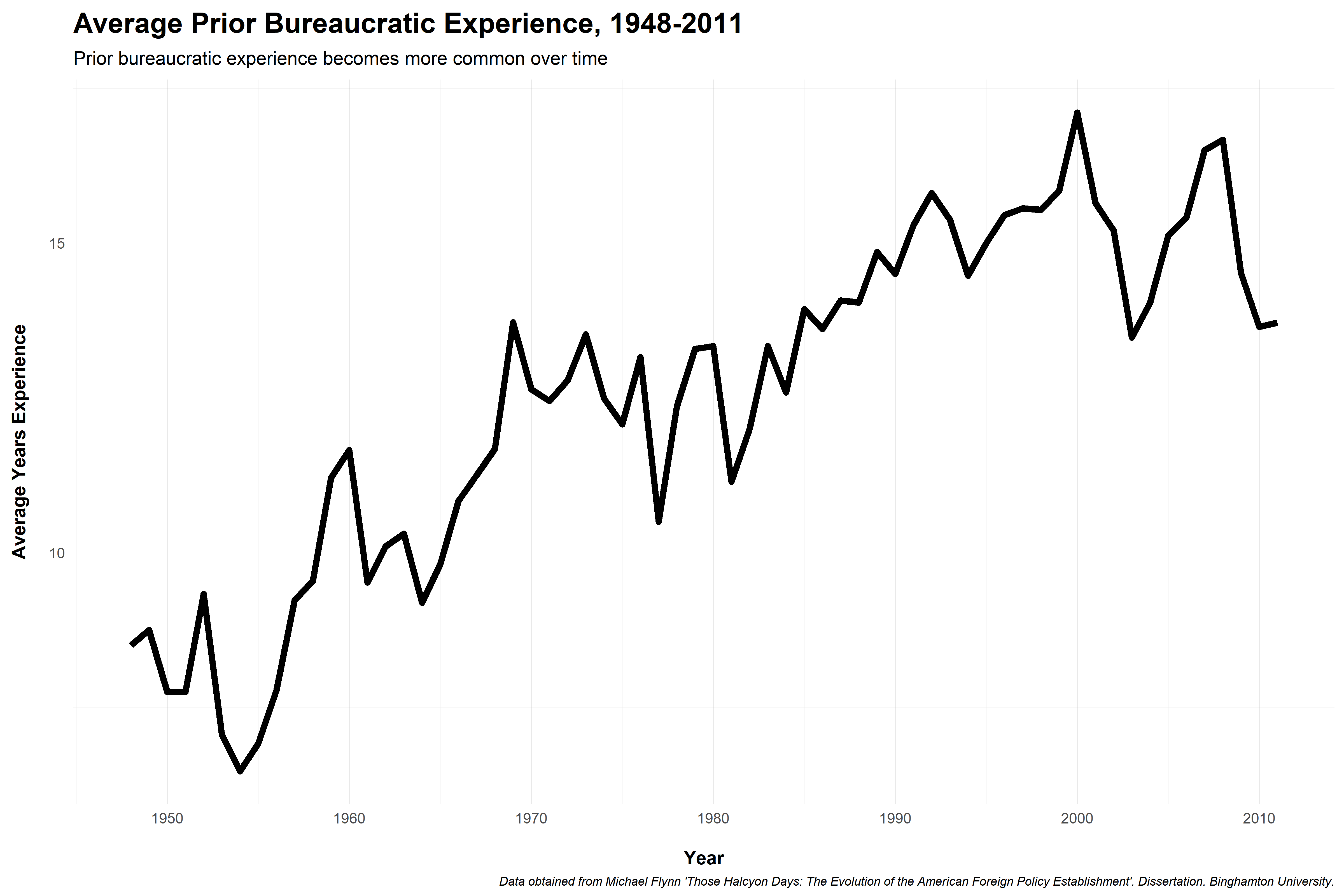
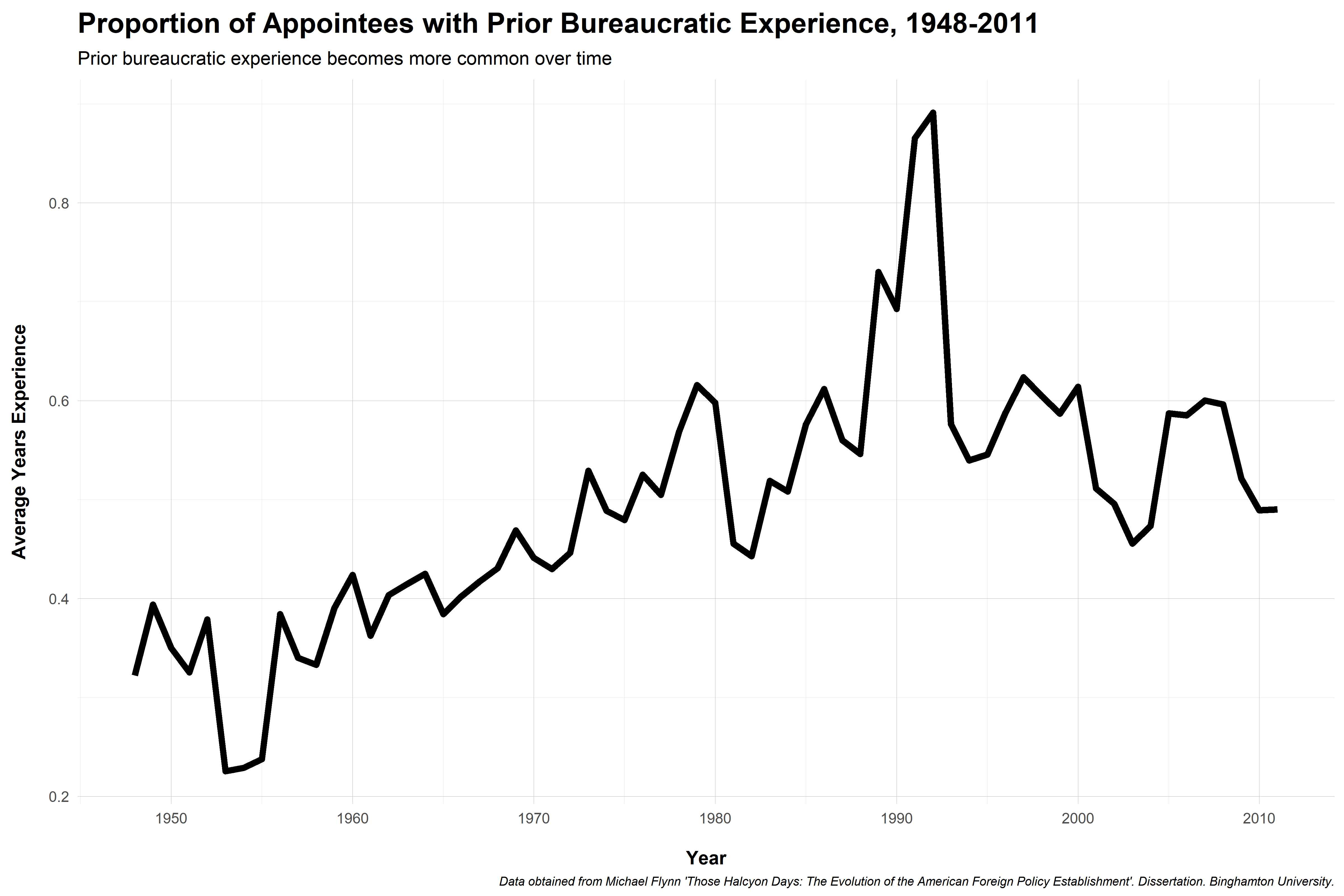
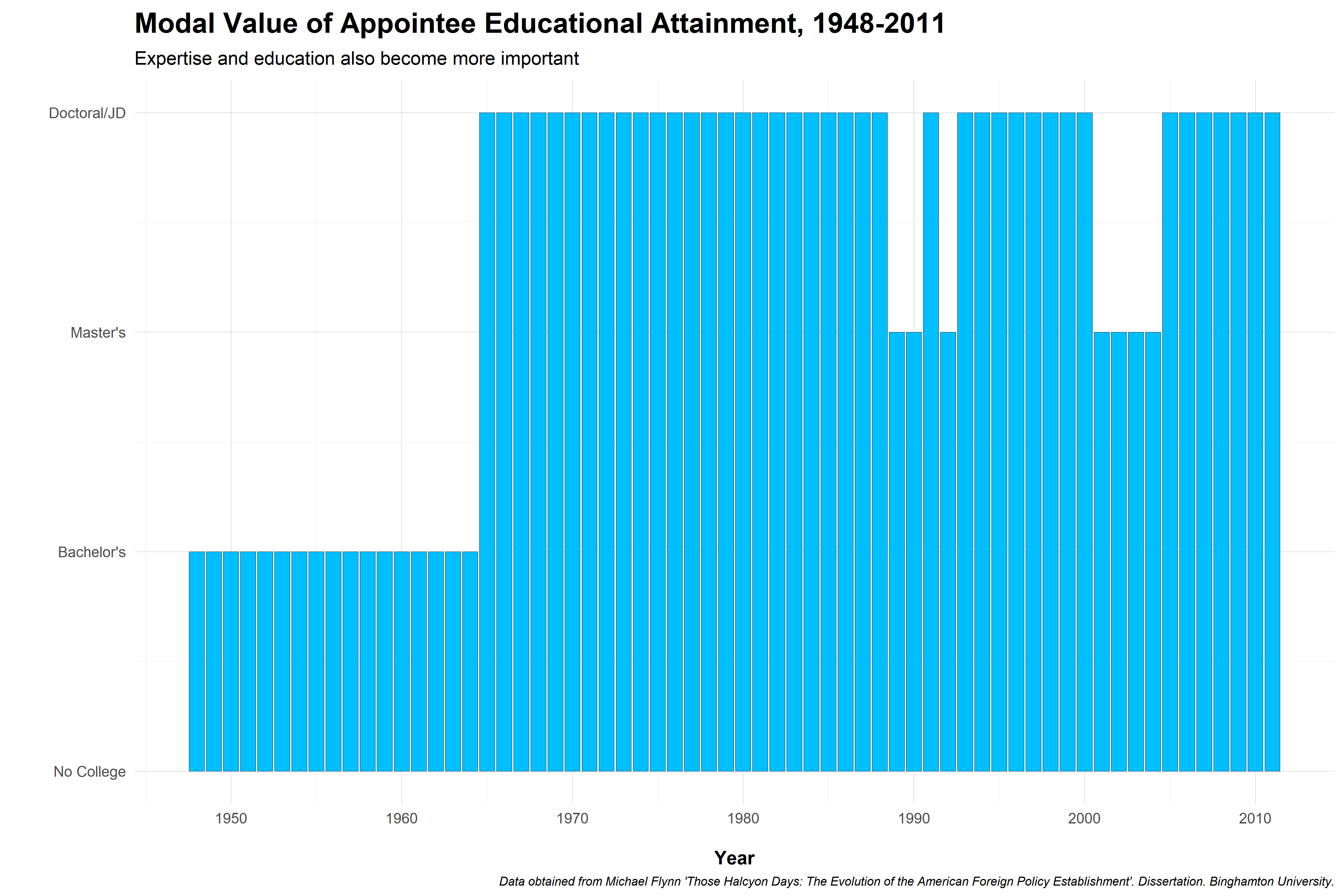
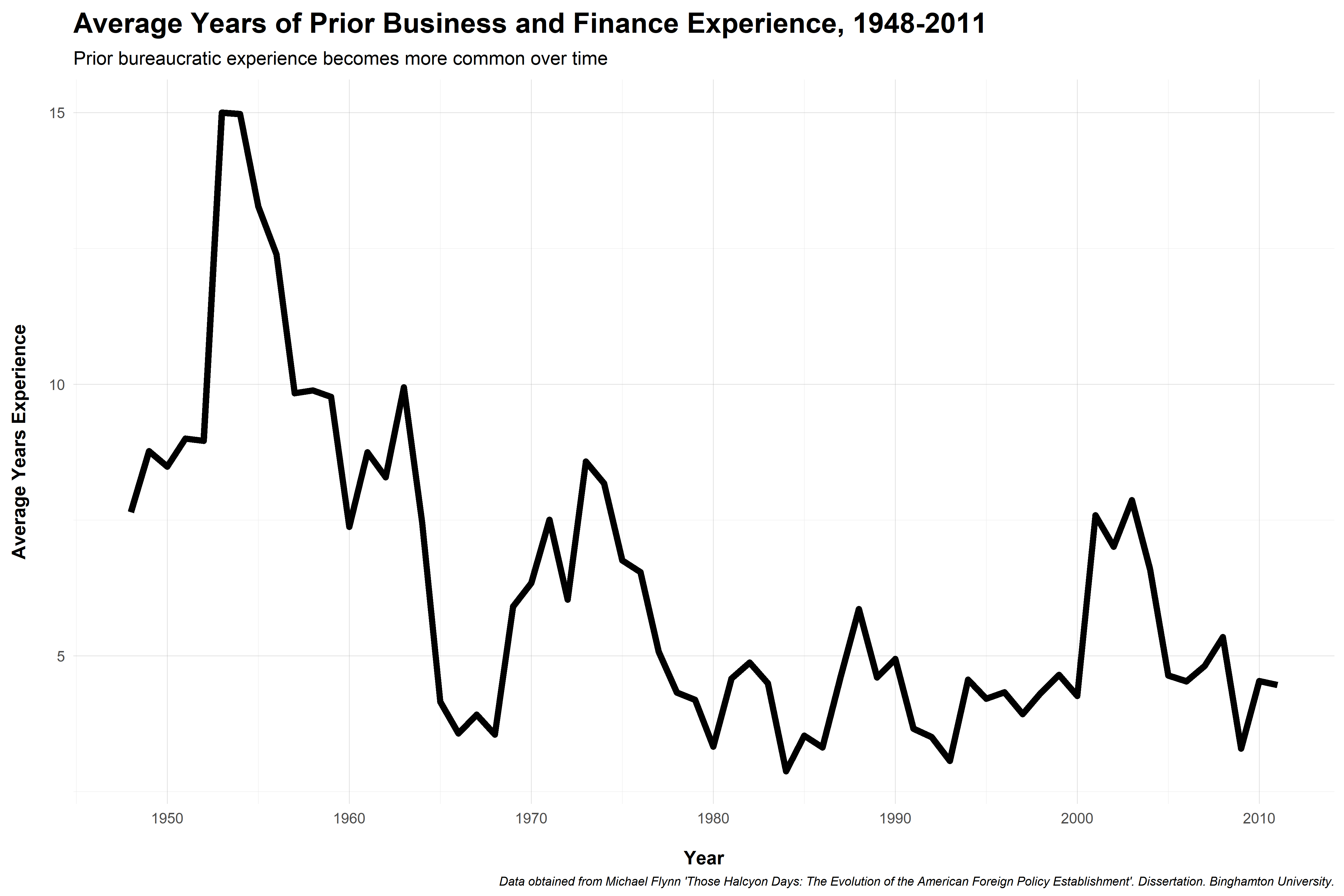
Foreign policy activism spurs demand for personnel, expertise
Senior administrators up through World War II generall had little government experience
Bureaucracy didn't become a "career" until post-1940s
What Are Bureaucracies?
What they do:
Day-to-day management and operations of the government
Help to formulate policies
Provide expertise and advice in different policy areas
Coordinate actions of various bureaucratic actors
Execute and implement policies
What Are Bureaucracies?
Functional Differentiation:
The specialization of different governmental units
Works at different levels:
State Department vs Defense Department
Navy vs Army
Artillery vs Armor
What Are Bureaucracies?
Different bureaucratic agencies
- State Department
- Defense Department
- Treasury Department
- Department of Energy
- Department of Homeland Security
- Department of Commerce
- Department of Agriculture
- US Agency for International Development
- Department of Labor
- FBI
- NSA
- Army
- Navy
- Air Force
- Marine Corps
- Coast Guard
- National Guard
- CIA
- DIA
- Customs and Border Patrol
- US Postal Service
- NASA
Bureaucracy has a reputation for redundancy...

And waste...

Why Do Bureaucracies Matter?
Why Do Bureaucracies Matter?
They're responsible for a lot...
Presidents make thousands of appointments after entering office
Hundreds of these relate to foreign policymaking
Direct presidential involvement varies
Personal taste
Big three: State, Defense, Treasury
Subordinates?
Why Do Bureaucracies Matter?
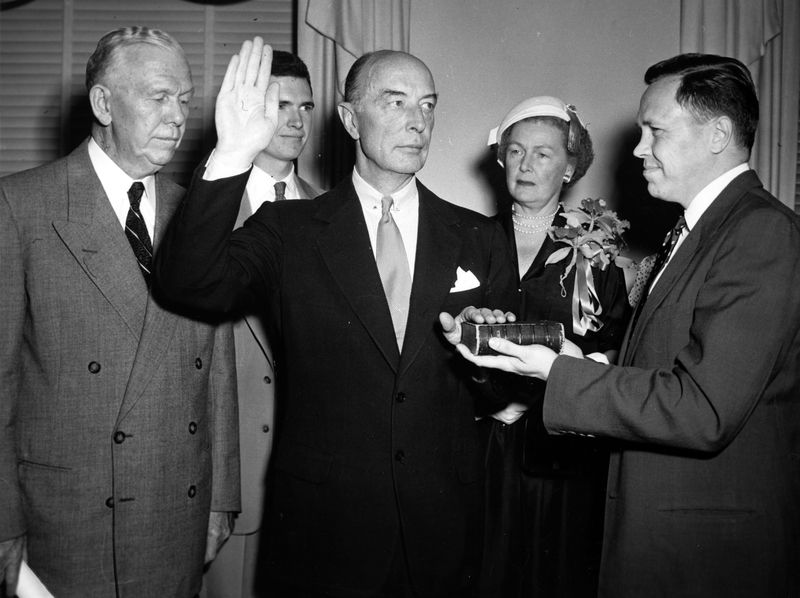
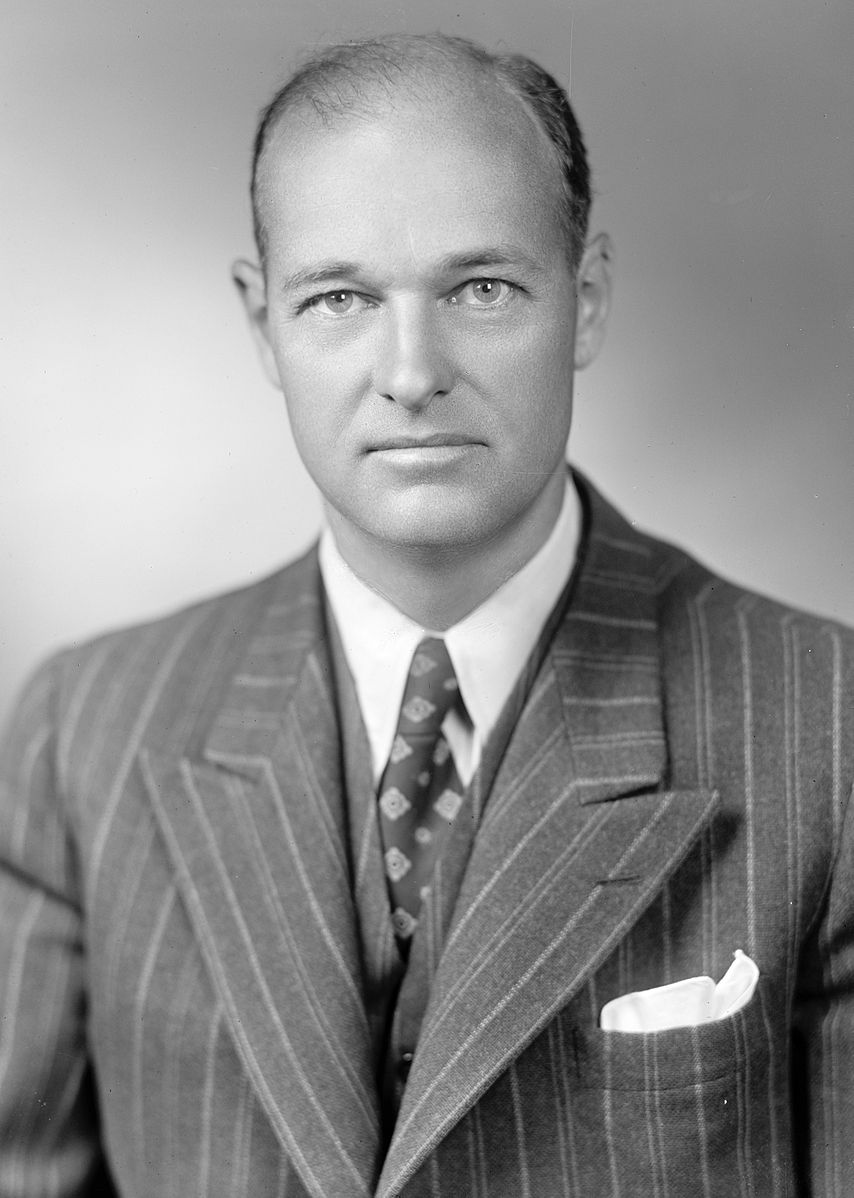
Robert Lovett:
Undersecretary of State
Deputy Secretary of Defense
Secretary of Defense
Lovett was given his choice of State, Defense, or Treasury by President Kennedy.
To right: Robert Lovett (a Republican) is sworn in as President Truman's (a Democrat) Secretary of Defense on September 17, 1951.

Why Do Bureaucracies Matter?
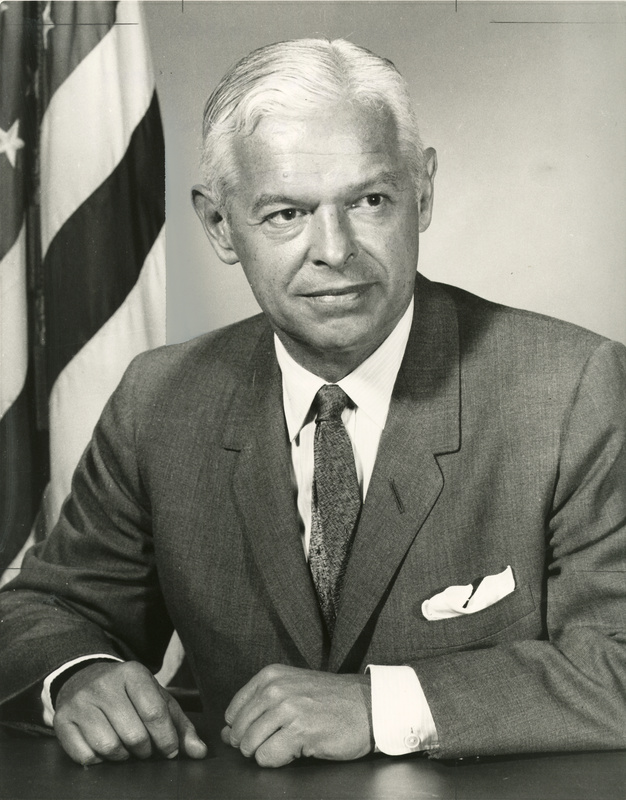
Paul Nitze:
Secretary of the Navy
Assistant Secretary of Defense for International Security Affairs
Director of State Department Policy Planning Staff
Deputy Secretary of Defense
Principal author of NSC-68

Why Do Bureaucracies Matter?
Power and influence
Principals
Deputies
Issue Area
Prestige
Position in bureaucratic hierarchy doesn't always match influence






Why Do Bureaucracies Matter?
Organizational and individuals motivations and goals
Fulfill organization's basic operational mandates/missions
Advance the interests of their organization
Fulfill basic responsibilities of individual position
Advance personal interests and power
Why Do Bureaucracies Matter?
Common Problems
Capture
Stove-piping
Groupthink
Turf battles
Slow adaptation


The State Department
The State Department
The Secretary of State is the chief diplomat of the Untied States
Supposed to be the principal adviser to the president on foreign affairs
Provides expertise and information on a variety of policy questions and geographic areas
Responsible for embassies and diplomats around the world
The State Department
Ambassadors
Position of ambassador is relatively new
Created in 1893
"Minister" was formerly the highest ranking diplomatic position for the United States
Ambassadorships awarded to country/region exports, but also to political allies
To right: Former US Ambassador to the United Kingdom, Matthew Barzun. Barzun also worked on President Obama's campaign.

The State Department
Historically the primary foreign policymaking body
Secretaries of State were very influential
Prominent officeholders include:
- Thomas Jefferson (to right)
- James Madison
- James Monroe
- John Quincy Adams
- Martin Van Buren
- James Buchanan

The State Department
Dean Acheson
Secretary of State Under President Truman
Epic Mustache
Targeted during the Red Scare by Congressional Republicans. The State Department was the subject of intense criticism by Republicans who claimed that communists had infiltrated the US government.





The State Department
State in decline
Basic organizational mandate
Organizational structure
Emphasized qualities of Foreign Service Officers
Gaps between Washington and local offices
Growth of alternative organizations/offices